/*
UDP NTP Client for STM32F103 with W5x000 Module
W5x00 <--> STM32F103 Pinout
SS <--> PA4
BOARD_SPI1_NSS_PIN
SCLK <--> PA5 BOARD_SPI1_SCK_PIN
MISO <--> PA6 BOARD_SPI1_MISO_PIN
MOSI <--> PA7 BOARD_SPI1_MOSI_PIN
3.3v <--> 3.3V
GND <--> GND
RST <--> PullUp
*/
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Ethernet_STM.h> //
https://github.com/rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32
#include <EthernetUdp.h> //
https://github.com/rogerclarkmelbourne/Arduino_STM32
#include <Dns.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
// https://github.com/PaulStoffregen/Time
// Enter a MAC address for your controller below.
// Newer Ethernet shields have a MAC address printed on a
sticker on the shield
#if defined(WIZ550io_WITH_MACADDRESS) // Use assigned MAC
address of WIZ550io
;
#else
#if defined(W5100_ETHERNET_SHIELD)
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0x51
};
#else
byte mac[] = { 0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0x55
};
#endif
#endif
#define NTP_SERVER "pool.ntp.org"
unsigned int localPort =
8888; // local port to
listen for UDP packets
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp is in
the first 48 bytes of the message
byte packetBuffer[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold
incoming and outgoing packets
// A UDP instance to let us send and receive packets over
UDP
EthernetUDP Udp;
// Time of last packet transmission(ms)
unsigned long lastSendPacketTime = 0;
// dow_char() 曜日文字を戻す [Sun,Mon....]
char * dow_char_EN(byte days) {
char *you[] = {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu",
"Fri", "Sat"};
return you[days];
}
// dow_char() 曜日文字を戻す [日曜,火曜....]
char * dow_char_JP(byte days) {
char *you[] = {"日曜", "月曜", "火曜", "水曜", "木曜", "金曜",
"土曜"};
return you[days];
}
// dow() 曜日を示す数値を戻す[0-Sunday, 1-Monday etc.]
uint8_t dow(unsigned long t) {
return ((t / 86400) + 4) % 7;
}
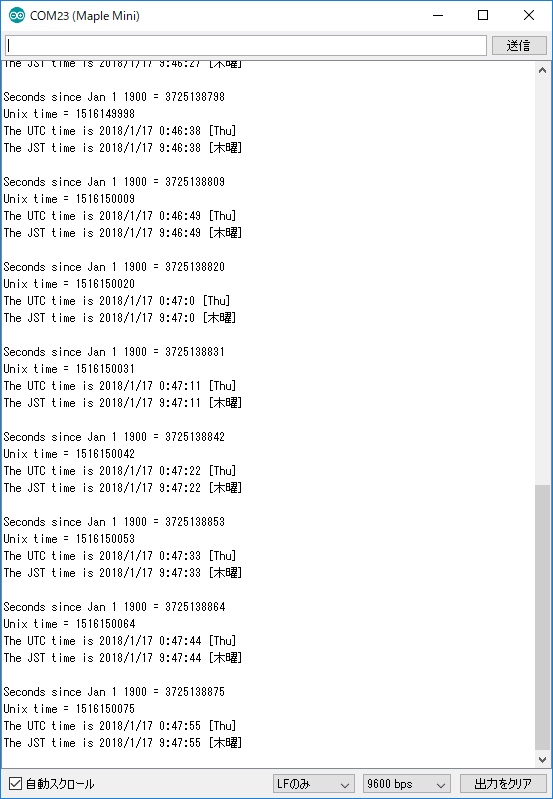
void showTime(char * title, time_t timet, char * dow) {
Serial.print(title);
Serial.print(year(timet));
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(month(timet));
Serial.print("/");
Serial.print(day(timet));
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(hour(timet));
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute(timet));
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(second(timet));
Serial.print(" [");
Serial.print(dow);
Serial.println("]");
}
void sendNTPpacket()
{
// set all bytes in the buffer to 0
memset(packetBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
// Initialize values needed to form NTP request
// (see URL above for details on the packets)
packetBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI,
Version, Mode
packetBuffer[1] = 0; //
Stratum, or type of clock
packetBuffer[2] = 6; //
Polling Interval
packetBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock
Precision
// 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root
Dispersion
packetBuffer[12] = 49;
packetBuffer[13] = 0x4E;
packetBuffer[14] = 49;
packetBuffer[15] = 52;
// all NTP fields have been given values, now
// you can send a packet requesting a
timestamp:
Udp.beginPacket(NTP_SERVER, 123); //NTP requests
are to port 123
Udp.write(packetBuffer,NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
Udp.endPacket();
return;
}
void setup()
{
// Open serial communications and wait for port to
open:
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("\n[NTP Client for EW5x00]");
// start Ethernet and UDP
#if defined(WIZ550io_WITH_MACADDRESS)
if (Ethernet.begin() == 0) {
#else
if (Ethernet.begin(mac) == 0) {
#endif
Serial.println("Failed to configure
Ethernet using DHCP");
// no point in carrying on, so do
nothing forevermore:
for (;;)
;
}
Serial.print("My IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
Serial.print("Netmask: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.subnetMask());
Serial.print("GW IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.gatewayIP());
Serial.print("DNS IP: ");
Serial.println(Ethernet.dnsServerIP());
#if defined(WIZ550io_WITH_MACADDRESS)
byte mac_address[6] ={0,};
W5100.getMACAddress(mac_address);
Serial.print("MAC: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
Serial.print("0x");
Serial.print(mac_address[i],HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
#endif
// タイムサーバーの名前解決
DNSClient dns;
IPAddress ServerIP;
dns.begin(Ethernet.dnsServerIP());
//
if(dns.getHostByName("ntp.jst.mfeed.ad.jp",ServerIP)
== 1) {
if(dns.getHostByName(NTP_SERVER,ServerIP) == 1) {
Serial.println(F("dns lookup
success"));
} else {
Serial.println(F("dns lookup failed"));
while(1) { }
}
Udp.begin(localPort);
}
void loop()
{
long now = millis();
if (now - lastSendPacketTime > 5000) { // 5
seconds passed
lastSendPacketTime = now;
sendNTPpacket();
}
// wait to see if a reply is available
delay(1000);
if ( Udp.parsePacket() ) {
Serial.println();
// We've received a packet, read the
data from it
Udp.read(packetBuffer,
NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read the packet into the buffer
//the timestamp starts at byte 40 of
the received packet and is four bytes,
// or two words, long. First, esxtract
the two words:
unsigned long highWord =
word(packetBuffer[40], packetBuffer[41]);
unsigned long lowWord =
word(packetBuffer[42], packetBuffer[43]);
// combine the four bytes (two words)
into a long integer
// this is NTP time (seconds since Jan
1 1900):
unsigned long secsSince1900 = highWord
<< 16 | lowWord;
Serial.print("Seconds since Jan 1 1900
= " );
Serial.println(secsSince1900);
// now convert NTP time into everyday
time:
// Unix time starts on Jan 1 1970. In
seconds, that's 2208988800:
const unsigned long seventyYears =
2208988800UL;
// subtract seventy years:
unsigned long epoch = secsSince1900 -
seventyYears;
// print Unix time:
Serial.print("Unix time = ");
Serial.println(epoch);
#if 0
// print the hour, minute and second:
Serial.print("The UTC time is
"); // UTC is the time
at Greenwich Meridian (GMT)
Serial.print((epoch % 86400L) /
3600); // print the hour (86400 equals secs per day)
Serial.print(':');
if ( ((epoch % 3600) / 60) < 10 ) {
// In the first 10 minutes
of each hour, we'll want a leading '0'
Serial.print('0');
}
Serial.print((epoch % 3600) /
60); // print the minute (3600 equals secs per minute)
Serial.print(':');
if ( (epoch % 60) < 10 ) {
// In the first 10 seconds
of each minute, we'll want a leading '0'
Serial.print('0');
}
Serial.println(epoch % 60); // print
the second
#endif
// グリニッジ標準時間
uint8_t DayOfWeek = dow(epoch);
showTime("The UTC time is ", epoch,
dow_char_EN(DayOfWeek));
// 日本標準時にあわせるために+9時間しておく
DayOfWeek = dow(epoch + (9 * 60 * 60));
showTime("The JST time is ", epoch + (9
* 60 * 60), dow_char_JP(DayOfWeek));
}
}
|